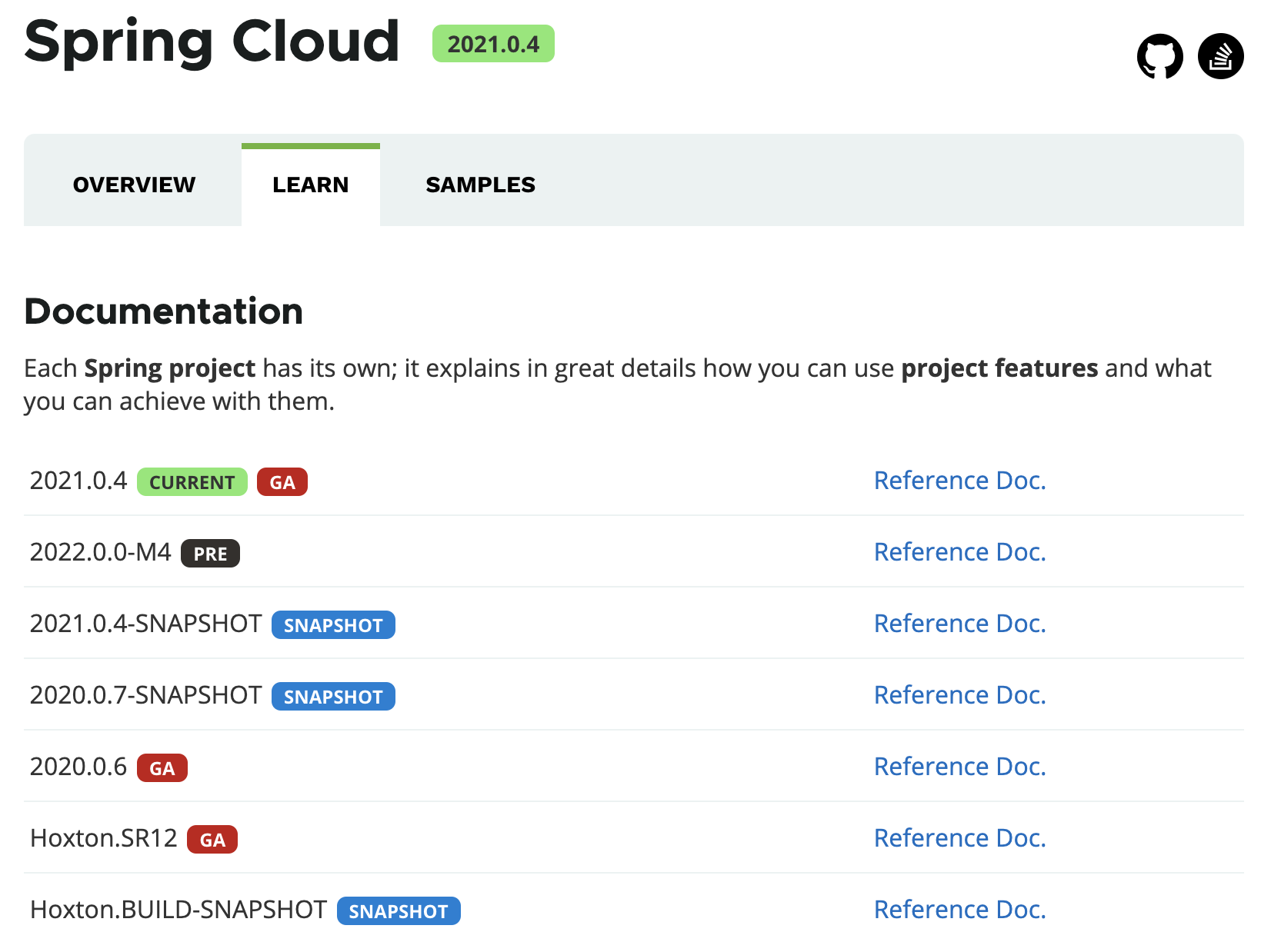
@EnableAsync
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(AsyncConfigurationSelector.class)
<!-- more -->
public @interface EnableAsync {
Class<? extends Annotation> annotation() default Annotation.class;
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
@EnableAsync注解即开启Spring对方法异步执行的能力,需要和注解@Configuration配合使用。
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AppConfig {
}
也可以自定义线程池
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AppConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(7);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(42);
executor.setQueueCapacity(11);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("MyExecutor-");
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
@Override
public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return MyAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler();
}
}
@Async
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Async {
String value() default "";
}
在要异步执行的方法上使用@Async注解,下面是一个没有返回值,一个带有返回值的异步调用的示例。
@Component
public class AsyncTask {
@Async
public void task1() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Async
public Future<String> task2() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new AsyncResult<String>("javastack");
}
}
测试代码
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class AsyncTest {
private final static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AsyncTest.class);
@Autowired
private AsyncTask asyncTask;
@Test
public void testTask1(){
log.info("start");
asyncTask.task1();
log.info("finish");
}
@Test
public void testTask2() {
log.info("start");
Future<String> future = asyncTask.task2();
while (true) {
if (future.isDone()) {
try {
log.info("result is " + future.get());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
}
}
log.info("finish");
}
}
注意事项
1、使用注意
@Async只能使用到被代理的对象方法上,即代理类的入口方法处,且方法必须是public的。
2、事务处理机制
使用@Async异步注解不能和@Transaction事务注解在同一个方法上同时使用,不然事务注解将无效。
要使用事务,需要把事务注解提取到方法里面的子方法上。
欢迎大家转发到朋友圈,和朋友们一起提升自己。
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。